10KN digital iron ore pellet compression testing machine
1. The main purpose of the pellet compression testing machine
The pellet compression testing machine is mainly used for pressure crushing test of various coking ore, and it can also be used for pressure test of other brittle materials. Comply with GB/T14201 "Method for Determination of Compressive Strength of Iron Ore Pellets", ISO4700 blast furnace and iron ore pellets for direct reduction feedstock---Determination of compressive strength, etc.

This machine is a mechatronics structure. Using micro-processing technology, load cell measuring force, high measuring accuracy.

The sophisticated automatic control and data acquisition system realizes the fully digital adjustment of the data acquisition and control process. The microcomputer controller automatically calculates the maximum bearing capacity, strength and other data, and displays the corresponding test results at the same time, and automatically saves them. The test parameters can be queried and displayed after the test is over, and can also be printed (optional for micro printer).
It has the function of returning to the initial position after the test, which is intelligent, efficient and fast.
It has limit protection function and overload and over current protection function at any working position, which is reliable and safe.
2. The main technical parameters of the testing machine
1 | Maximum test force | 10KN |
2 | Test force resolution | 0.01N |
3 | Relative error of indication | Better than ±1% in the range of 1%-100% |
4 | Moving speed of beam | 0.2-500mm/min |
5 | Moving stroke of beam | 0-400mm |
6 | Test machine span | 400mm |
7 | Diameter of upper indenter | 40mm |
8 | Lower pressure plate diameter | 100mm |
9 | voltage | 220V±10%, 50Hz |
10 | Motor Power | 0.75Kw |
11 | External dimensions of testing machine | 660X410X800mm |
12 | Test machine weight | 180kg |
How to Select the Right Tensile, Compression, Bending, Shear, Peel, and Tear Testing Machine: Calculation Formulas with Examples
Selecting the appropriate testing machine for tensile, compression, bending, shear, peel, and tear tests requires careful consideration of multiple factors, including the force range, specimen dimensions, test standards, and machine capabilities. Below are the key calculation formulas to help determine the necessary machine specifications, along with examples for better understanding.
1. Tensile Testing Machine Selection
Tensile testing machines measure the maximum tensile strength and elongation of materials.
Key Formula:
Fmax=σmax × A
Where:
Fmax = Maximum required force (N)
σmax = Ultimate tensile strength of the material (MPa)
A = Cross-sectional area of the specimen (mm²)
Example: For a steel specimen with σmax =400MPa and cross-sectional area A =100mm²:
Fmax=400 × 100=40,000N (40kN)
A 50 kN tensile testing machine would be suitable.
2. Compression Testing Machine Selection
Compression tests determine a material's resistance to compressive forces.
Key Formula:
Fmax=σc × A
Where:
Fmax = Maximum required force (N)
σc = Compressive strength of the material (MPa)
A = Cross-sectional area of the specimen (mm²)
Example: For a concrete cube with σc =30MPa and A =1502=22,500mm²:
Fmax=30 × 22,500=675,000N (675kN)
A 1000 kN compression testing machine would be ideal.
3. Bending Testing Machine Selection
Bending tests evaluate the flexural strength of materials.
Key Formula for Three-Point Bending:
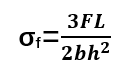
Where:
σf = Flexural stress (MPa)
F= Applied force (N)
L= Span length (mm)
b= Width of the specimen (mm)
h= Thickness of the specimen (mm)
Example: For a wooden beam with L=500mm, b=50mm, h=25mm, and requiring a stress of 10 MPa:
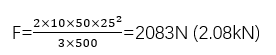
A 5 kN bending tester would be suitable.
4. Shear Testing Machine Selection
Shear tests determine the shear strength of materials.
Key Formula:
Fmax=τ × A
Where:
Fmax = Maximum shear force (N)
τ= Shear strength of the material (MPa)
A = Shear area (mm²)
Example: For an aluminum sheet with τ=90 MPa and A=200mm²:
Fmax=90×200=18,000N(18kN)
A 20 kN shear testing machine is recommended.
5. Peel Testing Machine Selection
Peel tests measure the adhesion strength between bonded materials.
Key Formula:
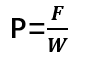
Where:
P= Peel strength (N/mm)
F= Measured force (N)
W= Width of the specimen (mm)
Example: For a tape with F=50N and W=25mm:
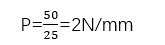
A peel testing machine with at least 5 N force capacity is required.
6. Tear Testing Machine Selection
Tear tests determine the resistance of a material to tearing forces.
Key Formula:
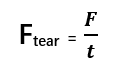
Where:
Ftear= Tear strength (N/mm)
F= Measured force (N)
t= Thickness of the specimen (mm)
Example: For a rubber sheet with F=100N and t=2mm:
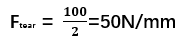
A tear testing machine with 100 N capacity is needed.
When selecting a testing machine, ensure that the maximum force capacity of the machine is at least 1.2 to 1.5 times the calculated force to account for safety margins and unexpected variations. Additionally, consider compliance with relevant test standards (ASTM, ISO, GB, EN, JIS) and machine features such as speed control, data acquisition, and test automation.
By using the above formulas and examples, engineers and manufacturers can accurately determine the appropriate testing machine specifications for their specific material and application requirements.
Categories
- electronic universal testing machine
- hydraulic universal testing machine
- impact testing machine
- compression testing machine
- horizontal tensile testing machine
- manhole cover testing machine
- pellet compression testing machine
- material testing machine
- steel strand tensile testing machine
- rubber testing equipment
- plastic testing equipment
- load cell
- Böhme abrasion tester
- all testing machine and equipment
- ceramic tiles testing equipment
- asphalt mixture testing equipment
- footwear testing machine
- test fixtures
- torsion tester
- cupping testing machine
- friction and wear tester
Contact Us
- +86-18615632092
- sophie@jnwtbte.com
- +86-18615632092














 售前客服
售前客服