YES-1000KN digital compression testing machine
1. Applications
This concrete compressive strength testing machine is to determine compressive strength of cylindrical concrete specimens and cubic concrete specimens by applying a compressive axial load to molded cylinders or cubic at a rate which is within a prescribed range until failure occurs. The compressive strength of the concrete specimen is calculated by dividing the maximum load attained during the test by the cross-sectional area of the specimen.
2.test method
GB/T 2611 testing machine General technical requirements
GB/T 3722 hydraulic pressure testing machine
GB/T 16825.1 Inspection of static single-axis testing machines - Part 1 : Examination and calibration of force measuring systems for tensile and compression testing machines
ISO 7500-1 metallic materials-verification of static uniaxial testing machines- parts 1: tension/compression testing machines-verification and calibration of the force-measuring system
ASTM E 74 practice of calibration of force-measuring instrument for verifying the force indication of testing machine
ASTM E4 Standard practice for force verification of testing machines
GB/T50081-2002 "Test methods for mechanical properties of ordinary concrete"
GB/T 4111 test method for the concrete block and brick
GB/T 11837 concrete compressive strength test method for concrete pipes
AASHTO T22 compressive strength of cylindrical concrete specimens
BS 1881 testing concrete
ASTM C39/C39M standard test method for compressive strength of cylindrical concrete specimens
EN 12390-3 testing hardened concrete- part 3: compressive strength of test specimens
ISO 1920-4 testing of concrete-part 4: strength of hardened concrete
3. Specifications for concrete compressive strength testing machine
1 | Force capacity | 1000KN |
2 | Accuracy of test force | <±1% |
3 | Space adjusting mode | Manual adjusting |
4 | Size of upper and lower compression platen | 220x300mm |
5 | Distance between upper and lower compress platen | 330mm |
6 | Piston stroke | 30mm |
7 | Piston diameter | 250mm |
8 | Rated pressure of oil pump | 40Mpa |
9 | Motor power | 0.75KW |
10 | Dimension | 820x550x1300mm |
11 | Weight | 750kg |
How to Select the Right Tensile, Compression, Bending, Shear, Peel, and Tear Testing Machine: Calculation Formulas with Examples
Selecting the appropriate testing machine for tensile, compression, bending, shear, peel, and tear tests requires careful consideration of multiple factors, including the force range, specimen dimensions, test standards, and machine capabilities. Below are the key calculation formulas to help determine the necessary machine specifications, along with examples for better understanding.
1. Tensile Testing Machine Selection
Tensile testing machines measure the maximum tensile strength and elongation of materials.
Key Formula:
Fmax=σmax × A
Where:
Fmax = Maximum required force (N)
σmax = Ultimate tensile strength of the material (MPa)
A = Cross-sectional area of the specimen (mm²)
Example: For a steel specimen with σmax =400MPa and cross-sectional area A =100mm²:
Fmax=400 × 100=40,000N (40kN)
A 50 kN tensile testing machine would be suitable.
2. Compression Testing Machine Selection
Compression tests determine a material's resistance to compressive forces.
Key Formula:
Fmax=σc × A
Where:
Fmax = Maximum required force (N)
σc = Compressive strength of the material (MPa)
A = Cross-sectional area of the specimen (mm²)
Example: For a concrete cube with σc =30MPa and A =1502=22,500mm²:
Fmax=30 × 22,500=675,000N (675kN)
A 1000 kN compression testing machine would be ideal.
3. Bending Testing Machine Selection
Bending tests evaluate the flexural strength of materials.
Key Formula for Three-Point Bending:
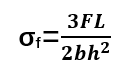
Where:
σf = Flexural stress (MPa)
F= Applied force (N)
L= Span length (mm)
b= Width of the specimen (mm)
h= Thickness of the specimen (mm)
Example: For a wooden beam with L=500mm, b=50mm, h=25mm, and requiring a stress of 10 MPa:
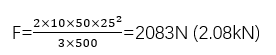
A 5 kN bending tester would be suitable.
4. Shear Testing Machine Selection
Shear tests determine the shear strength of materials.
Key Formula:
Fmax=τ × A
Where:
Fmax = Maximum shear force (N)
τ= Shear strength of the material (MPa)
A = Shear area (mm²)
Example: For an aluminum sheet with τ=90 MPa and A=200mm²:
Fmax=90×200=18,000N(18kN)
A 20 kN shear testing machine is recommended.
5. Peel Testing Machine Selection
Peel tests measure the adhesion strength between bonded materials.
Key Formula:
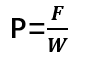
Where:
P= Peel strength (N/mm)
F= Measured force (N)
W= Width of the specimen (mm)
Example: For a tape with F=50N and W=25mm:
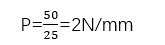
A peel testing machine with at least 5 N force capacity is required.
6. Tear Testing Machine Selection
Tear tests determine the resistance of a material to tearing forces.
Key Formula:
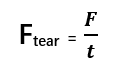
Where:
Ftear= Tear strength (N/mm)
F= Measured force (N)
t= Thickness of the specimen (mm)
Example: For a rubber sheet with F=100N and t=2mm:
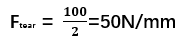
A tear testing machine with 100 N capacity is needed.
When selecting a testing machine, ensure that the maximum force capacity of the machine is at least 1.2 to 1.5 times the calculated force to account for safety margins and unexpected variations. Additionally, consider compliance with relevant test standards (ASTM, ISO, GB, EN, JIS) and machine features such as speed control, data acquisition, and test automation.
By using the above formulas and examples, engineers and manufacturers can accurately determine the appropriate testing machine specifications for their specific material and application requirements.
Categories
- electronic universal testing machine
- hydraulic universal testing machine
- impact testing machine
- compression testing machine
- horizontal tensile testing machine
- manhole cover testing machine
- pellet compression testing machine
- material testing machine
- steel strand tensile testing machine
- rubber testing equipment
- plastic testing equipment
- load cell
- Böhme abrasion tester
- all testing machine and equipment
- ceramic tiles testing equipment
- asphalt mixture testing equipment
- footwear testing machine
- test fixtures
- torsion tester
- cupping testing machine
- friction and wear tester
Contact Us
- +86-18615632092
- sophie@jnwtbte.com
- +86-18615632092









 售前客服
售前客服